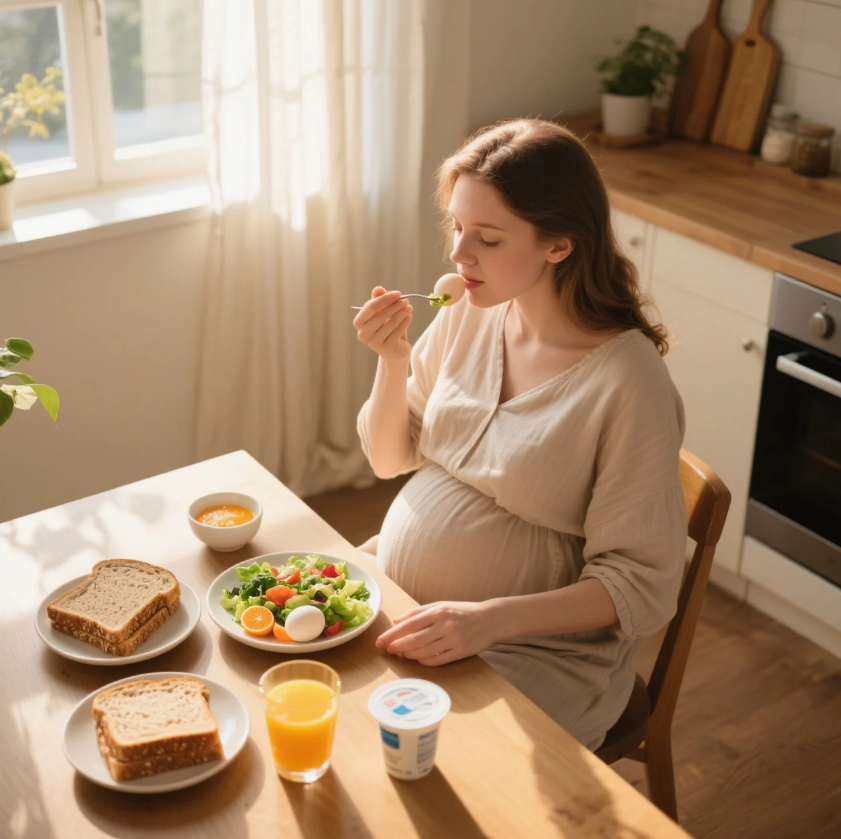
When you’re expecting, you’re not just eating for two—you’re nourishing the foundation of a new life. What you eat during pregnancy has a powerful impact on your baby’s development, your energy levels, and your overall well-being. But in the age of online overload, it’s easy to get lost in a maze of conflicting advice.
Let’s cut through the noise.
This article breaks down pregnancy nutrition into clear, science-backed guidance that goes beyond cliché lists. You’ll learn what to eat, what to avoid, and why it matters, all while keeping your taste buds (and your baby bump) happy.

Why Pregnancy Nutrition Matters More Than Ever
Pregnancy is a time of rapid growth and transformation. From the moment of conception, your body shifts into high gear—creating organs, tissues, bones, and brains. To fuel all this development, your baby draws essential nutrients from you. That means your diet becomes your baby’s diet.
Poor nutrition can increase risks of:
- Low birth weight
- Premature birth
- Developmental delays
- Gestational diabetes or high blood pressure
On the flip side, eating well can:
- Support brain and bone development
- Boost your immunity and mood
- Promote steady weight gain
- Set your child up for lifelong health
The Nutrients You Need (and Where to Get Them)
1. Folate (Folic Acid)
Why it’s important: Helps prevent neural tube defects like spina bifida, especially in the first trimester.
Best sources:
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Lentils and beans
- Fortified cereals
- Oranges
Pro tip: Even before you know you’re pregnant, folate is essential. Doctors recommend 400 to 800 mcg daily for all women of childbearing age.
2. Iron
Why it’s important: Carries oxygen in your blood to your baby. Your blood volume increases by about 50% during pregnancy, so iron needs spike.
Best sources:
- Lean red meat
- Spinach and kale
- Iron-fortified whole grains
- Dried fruits like apricots and raisins
Iron tip: Pair iron-rich foods with vitamin C (like orange juice) to boost absorption.
3. Calcium
Why it’s important: Builds strong bones and teeth—for your baby, not just you.
Best sources:
- Dairy (milk, yogurt, cheese)
- Leafy greens
- Almonds
- Fortified plant-based milk (soy, almond, oat)
If your diet is dairy-free, pay special attention to calcium intake or consider a supplement after consulting your doctor.
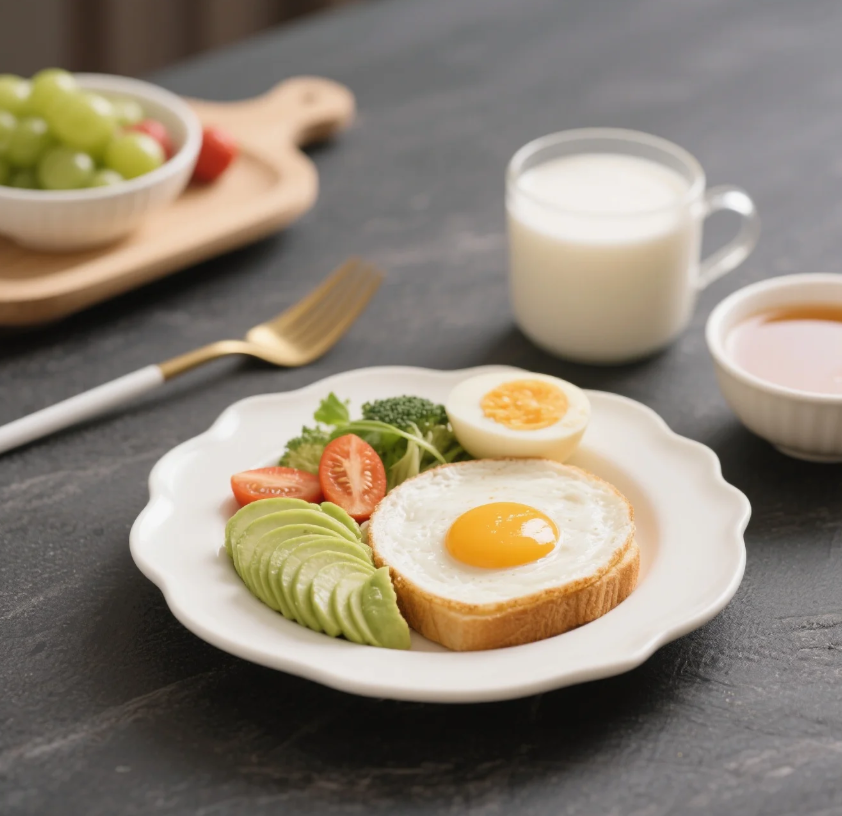

4. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Why it’s important: Essential for brain and eye development.
Best sources:
- Fatty fish (salmon, sardines)
- Flaxseeds and chia seeds
- Walnuts
Note: Stick to low-mercury fish and limit to 2–3 servings per week.
5. Protein
Why it’s important: Fuels tissue growth and helps form muscles and organs.
Best sources:
- Eggs
- Chicken
- Beans and lentils
- Tofu
- Greek yogurt
Aim for about 75 to 100 grams of protein daily, depending on your weight and trimester.
6. Fiber
Why it’s important: Prevents pregnancy constipation, supports digestion, and keeps blood sugar levels stable.
Best sources:
- Whole grains (oats, brown rice, quinoa)
- Fruits (berries, apples with skin)
- Vegetables (broccoli, carrots)
- Legumes
Drink plenty of water to help fiber do its job!
Foods to Embrace During Pregnancy
Let’s make your grocery list a little smarter. Here are some standout foods that deliver multiple pregnancy perks:
1. Avocados
Rich in healthy fats, folate, and potassium. Also helps reduce leg cramps.
2. Eggs
A protein powerhouse with choline, crucial for baby’s brain development.
3. Greek Yogurt
Loaded with calcium, protein, and probiotics that support gut health.
4. Berries
Packed with antioxidants, fiber, and vitamins. Add them to smoothies or oatmeal.
5. Sweet Potatoes
High in beta-carotene (which turns into vitamin A), essential for fetal growth.
6. Nuts and Seeds
Great snacks that provide healthy fats, iron, and magnesium.
7. Whole Grains
Brown rice, oats, and quinoa deliver energy and help manage blood sugar levels.
Foods to Avoid (And Why They Matter)
Not every food is safe during pregnancy. Some can contain bacteria, parasites, or high levels of harmful substances. Here’s a breakdown of the no-go list:
1. Raw or Undercooked Meat and Eggs
Can carry salmonella or listeria. Always cook meats and eggs thoroughly.
2. Unpasteurized Dairy and Juices
Risk of listeria infection, which can lead to miscarriage or stillbirth. Check labels carefully.
3. High-Mercury Fish
Avoid swordfish, king mackerel, shark, and tilefish. Mercury can harm fetal brain development.
4. Deli Meats and Hot Dogs (Unless Heated)
May contain listeria unless heated until steaming hot.
5. Alcohol
No safe level of alcohol during pregnancy has been established. Even occasional drinking can impact development.
6. Excess Caffeine
Limit caffeine to 200 mg per day (about one 12-oz cup of coffee). Too much can raise the risk of miscarriage or low birth weight.
7. Raw Sprouts (like alfalfa, mung bean)
Can harbor bacteria that survive even with washing. Cook before eating.
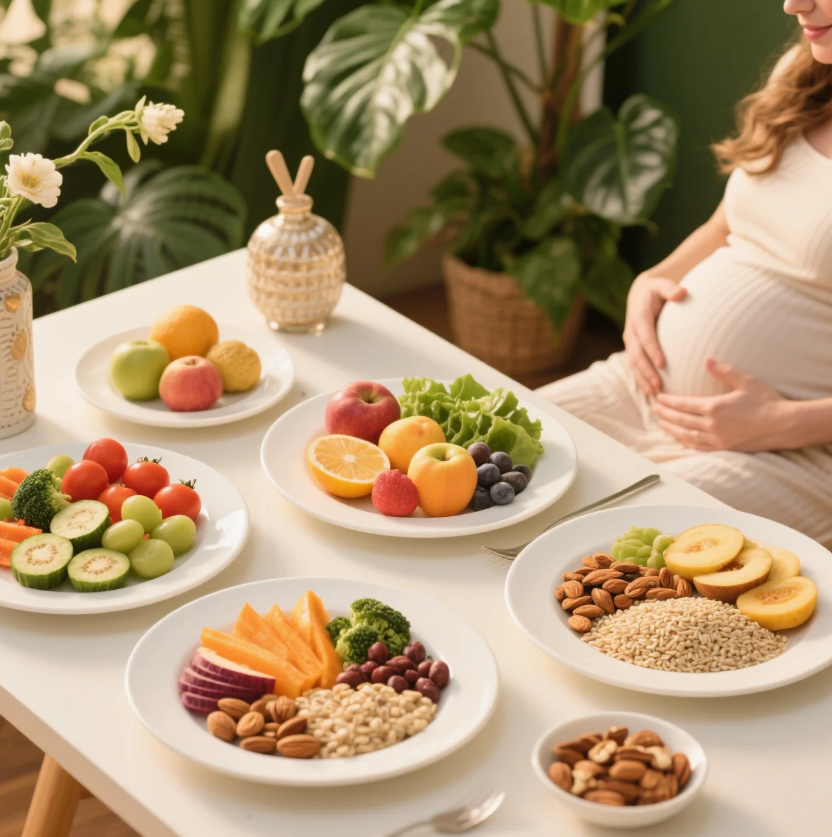

Debunking Pregnancy Food Myths
Myth 1: “You’re eating for two.”
Truth: You only need about 300 extra calories a day in the second and third trimester. That’s an extra snack—not a second dinner.
Myth 2: “Cravings mean your body needs that food.”
Truth: Cravings aren’t always rooted in nutritional need. Wanting pickles and ice cream might just be hormones doing their thing.
Myth 3: “All seafood is unsafe.”
Truth: Low-mercury fish like salmon and sardines are actually encouraged. Just be mindful of portion sizes.
Practical Tips for Building a Pregnancy-Friendly Diet
- Meal Prep in Batches: Keep healthy meals ready when fatigue hits.
- Snack Smart: Keep nuts, fruit, or yogurt handy for quick hunger fixes.
- Hydrate Regularly: Aim for 8–12 glasses of water daily to support amniotic fluid levels and digestion.
- Balance Your Plate: Follow the “half veggies, quarter protein, quarter carbs” rule when you can.
- Listen to Your Body: It’s normal to have food aversions or nausea. Eat what you can, when you can.
Should You Take Supplements?
Even with the healthiest diet, most OB-GYNs recommend a prenatal vitamin to fill any nutritional gaps. Look for one that includes:
- Folic acid
- Iron
- DHA (for brain development)
- Vitamin D
- Calcium
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting or changing any supplement.
When to Talk to a Professional
If you’re dealing with morning sickness, gestational diabetes, food allergies, or any digestive issues, you may benefit from consulting a registered dietitian. Personalized nutrition plans can make a huge difference.
Final Thoughts
Pregnancy isn’t about achieving perfection—it’s about creating a nurturing environment for you and your baby. Eating well doesn’t mean overthinking every bite. It means making consistent, smart choices that add up over time.
So go ahead, snack on that Greek yogurt, cook up a colorful stir-fry, and sip your lemon water with pride. You’re doing something amazing—and your plate is part of that journey.
Your baby’s first taste of the world begins with you. Make it delicious, make it nourishing, and most of all—make it joyful.